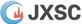Introduction
In the field of extractive metallurgy, mineral extraction is that the process of separating commercially valuable minerals from their ores, it involves two step, out of which one is comminution, and another is separation. The comminution is the process of crushing and size wise screening. crushing is the first stage of mineral extraction where the ore fed into the size reduction equipment as as to reduce the size for subsequent processing by liberating the target mineral from the gangue. Crushing is generally the first stage process of preparation of a rock mass for ore beneficiation. On this website, crushing refers only to the process of rough splitting the rock after drilling and blasting operations.

Mineral processing generally involve four operation stages. They are: 1) Comminution — rock size reduction; 2) Screening — separating particle sizes by screening or classification; 3) Concentration — gravity separation, magnetic separation, flotation separation and so on methods 4) Dewatering — solid/liquid separation.
Comminution & Crushing
Comminution is the process of mineral size reduction. Comminution process is generally involves crushing and grinding, the minerals forms can be dry or slurries. The crushing is usually acts on the ROM, and mainly done by the rock crushers; and the grinding is usually carried out after crushing, done by the grinding mills.
Compression, impact and attrition forces Based on the crushing mechanism, the comminution is mainly done by three types of forces: compression, impact and attrition. Compression force and impact force are mainly used in crushing operations, while attrition force is the dominant force in grinding operations. In the field of mineral processing, the crushing equipment designed based on compressive force and impact force includes jaw crusher, rotary crusher, cone crusher and impact crusher, and grinding machine based on attrition force includes rod mill and ball mill.
Crushing stages
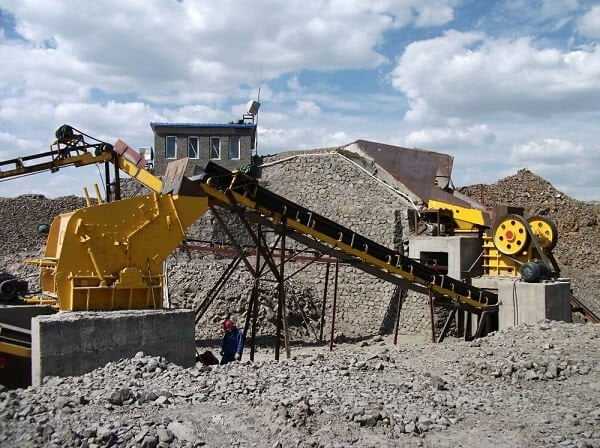
All crushers have a maximum crushing ratio, which means that material size reduction will be carried out in stages. The concept of crushing minerals in stages is still in use today. In this method, according to the hardness, size and type of minerals, special treatments are performed to extract the maximum value from each particle size fraction. The table below shows the steps from crushing to upgrading.
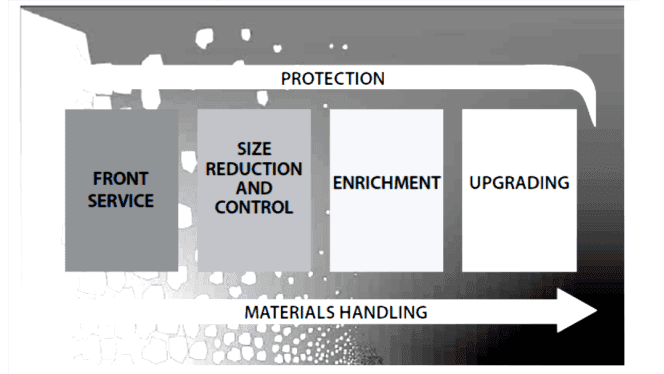
Crushing of minerals
Crushing is the most invested operation in mineral processing. The goal of crushing is to produce mineral fractions of required particle for subsequent benefication process. The quality parameters are usually hardness, size and shape. The figure shows the different size reduction stages from 1000mm to 4mm.
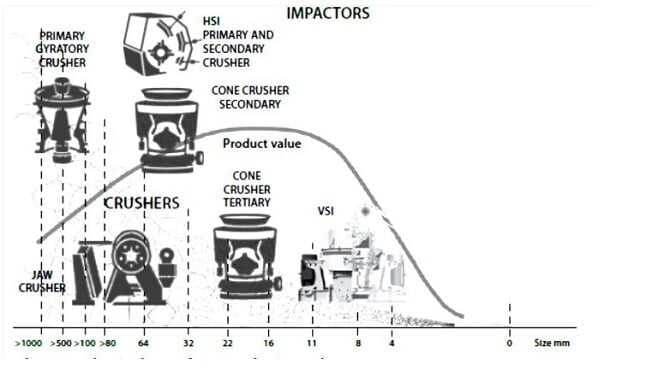 The reduction in ore size is to liberate valuable minerals from the host rock. This means that we must reduce the ore to a liberated size, usually between 100 and 10 microns. The crushing process is divided into three stages, namely the first stage, the second stage and the third stage. The reduction in the size range at each stage is called R1, R2 and R3. This picture shows the rock crushing equipment and reduction ratio at each stage.
The reduction in ore size is to liberate valuable minerals from the host rock. This means that we must reduce the ore to a liberated size, usually between 100 and 10 microns. The crushing process is divided into three stages, namely the first stage, the second stage and the third stage. The reduction in the size range at each stage is called R1, R2 and R3. This picture shows the rock crushing equipment and reduction ratio at each stage.
Types of crushers
The stone crushers are major size reduction equipment which crushes different types of soft and hard materials into smaller pieces that are more suitable for applications such as mechanical, metallurgical and allied industries. Crushers can reduce or change the form of waste, so they can be more easily processed or recycled, or reduce the size of solid raw materials (such as rock mines), so that different combinations can be distinguished. There are many types of rock crushers, including cone crusher, jaw crusher, impact crusher, hammer crusher and grinder.
According to the operation principle, the crushing equipment can be divided into impact crusher and laminated crusher. According to the hourly production capacity (t/h) of each crushing equipment, they can also be divided into three categories: Large crusher: the production capacity is between 300 and 1500 tons/hour; Medium crusher: the production capacity is between 100 and 300 tons/hour; Small crusher: the production capacity is between 0 and 100 tons/hour. There are other rotor-dependent classification methods, for example, a crusher with a single rotor and a dual rotor.
Jaw Crusher
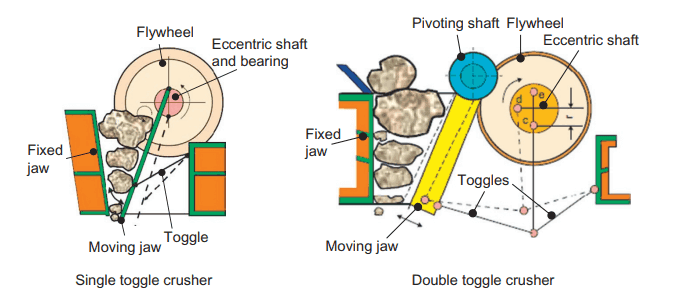
Jaw crusher is the main primary crusher used in the crushing circuit of ore and large blocks in the field of quarrying, mining industry. Jaw crusher is based on the mechanism of compression crushing. The material is crushed under the compression force in the wedge shaped pit by the movement of moving jaw.
The feed chamber of the jaw crusher is composed of a movable jaw and a fixed jaw. The raw ore is fed into the top of jaw crusher by the vibrating screen feeder. Movable jaws in motion crush the material imitating the two jaws of the animal to crush the material.
Cone Crusher
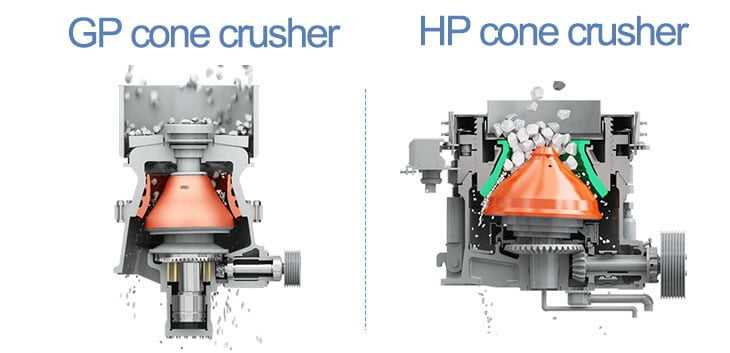
Cone crusher is suitable for crushing a variety of middle-hard and above middle-hard ores and rocks. With the constant development of crushing technology, various cone crushers types emerge, composite cone crushers, spring cone crushers, hydraulic cone crushers and rotary crushers. According to different models, cone crushers are divided into compond cone crushers, Symons cone crushers, single-cylinder hydraulic cone crushers, multi-cylinder hydraulic cone crushers, etc.
Impact Crusher
There are two types of impact crushers: horizontal shaft impactor (HSI) and vertical shaft impactor (VSI). Impact crushers are use impact force rather than compression force to crush material, the impact crusher is known as the secondary impact crusher, mainly used for the second stage of crushing. They are suitable for medium to hard rock.
This impact stone crusher is an efficient and powerful medium and coarse crushing equipment produced by our company. If the pressure of the material is less than 150Mpa, impact crushing can replace the jaw crusher and become the main crushing equipment. If the material pressure exceeds 150Mpa, impact crusher can be used for secondary crushing stage. The output size can be adjusted by changing the gap between the impact plate and the rotor. The biggest characteristic of the impact crusher is: the final particle size is cubic, without cracks, good shape. Impact rock crusher has a wide application fields like mining, railway, highway, cement, chemical, construction, etc.
Typical uses of main crushers
| Type | Hardness | Abrasion limit | Moisture content | Reduction ratio | Main use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound crusher | Medium hard to very hard | Abrasive | Dry or wet, not sticky | 3/1 to 5/1 | Mine, building materials |
| Cone crushers | Medium hard to very hard | Abrasive | Dry or wet, not sticky | 3/1 to 5/1 | Quarried materials, sand & gravel |
| Crusher buckets | Soft to very hard | No limit | Dry or wet and sticky | 3/1 to 5/1 | Heavy mining, quarried materials, sand & gravel, recycling |
| Gyratory crushers | Soft to very hard | Abrasive | Dry to slightly wet, not sticky | 4/1 to 7/1 | Heavy mining, quarried materials |
| Horizontal shaft impactors | Soft to medium hard | Slightly abrasive | Dry or wet, not sticky | 10/1 to 25/1 | Quarried materials, sand & gravel, recycling |
| Jaw crushers | Soft to very hard | No limit | Dry to slightly wet, not sticky | 3/1 to 5/1 | Heavy mining, quarried materials, sand & gravel, recycling |
| Mineral sizers | Hard to soft | Abrasive | Dry or wet and sticky | 2/1 to 5/1 | Heavy mining |
| Vertical shaft impactors (autogenous) | Soft to very hard | No limit | Dry or wet, not sticky | 2/1 to 5/1 | Quarried materials, sand & gravel |
| Vertical shaft impactors (shoe and anvil) | Medium hard to very hard | Slightly abrasive | Dry or wet, not sticky | 6/1 to 8/1 | Sand & gravel, recycling |
Conclusion
Whether it is carried out directly inside the mine or at a place where further processing is carried out, when extracting and processing raw materials, it is necessary to make correct preparations. The required size of crushing raw materials is the key to ensuring the final successful extraction of target minerals. Crushers can also be used to crush or medium hard rocks as well as cohesive and soft materials such as lignite and mineral coal, clay, marl, limestone and similar raw materials. According to the nature of the minerals, additional steps such as washing, sieving, etc. are added.