Graphite mainly refers to natural graphite, which is a non-metallic mineral formed by carbon under specific high-temperature reduction conditions, and is most commonly found in marble, schist, and gneiss. Graphite is an important industrial mineral. Graphite has many characteristics such as good high temperature resistance, thermal shock resistance, electrical conductivity, lubricity, chemical stability and plasticity, so it is widely used in steel, chemical, machinery, electronics, aerospace, national defense and military industries.
What Is Graphite?
According to the crystalline form of graphite, natural graphite can be divided into crystalline graphite and cryptocrystalline graphite. The crystal diameter of graphite is greater than 1μm, and the crystalline graphite crystal shape can be observed under the naked eye or under a common microscope. It is called crystalline graphite; the graphite crystal diameter is less than 1μm, and the dense graphite aggregates that are difficult to recognize under the microscope are called crystalline graphite. Cryptocrystalline graphite or amorphous graphite, because most cryptocrystalline graphite is black earthy, it is also called earthy graphite and microcrystalline graphite.
Graphite Beneficiation Plant
The graphite beneficiation process is mainly aimed at various graphite ore, pyrite or mica with different crystal forms. It adopts two combined beneficiation processes of multi-stage grinding and multi-stage flotation and gravity flotation. This solution is for a rock stone-type graphite processing plant. It is configured with crushing part, grinding, flotation, and concentrate concentration, and dehydration.
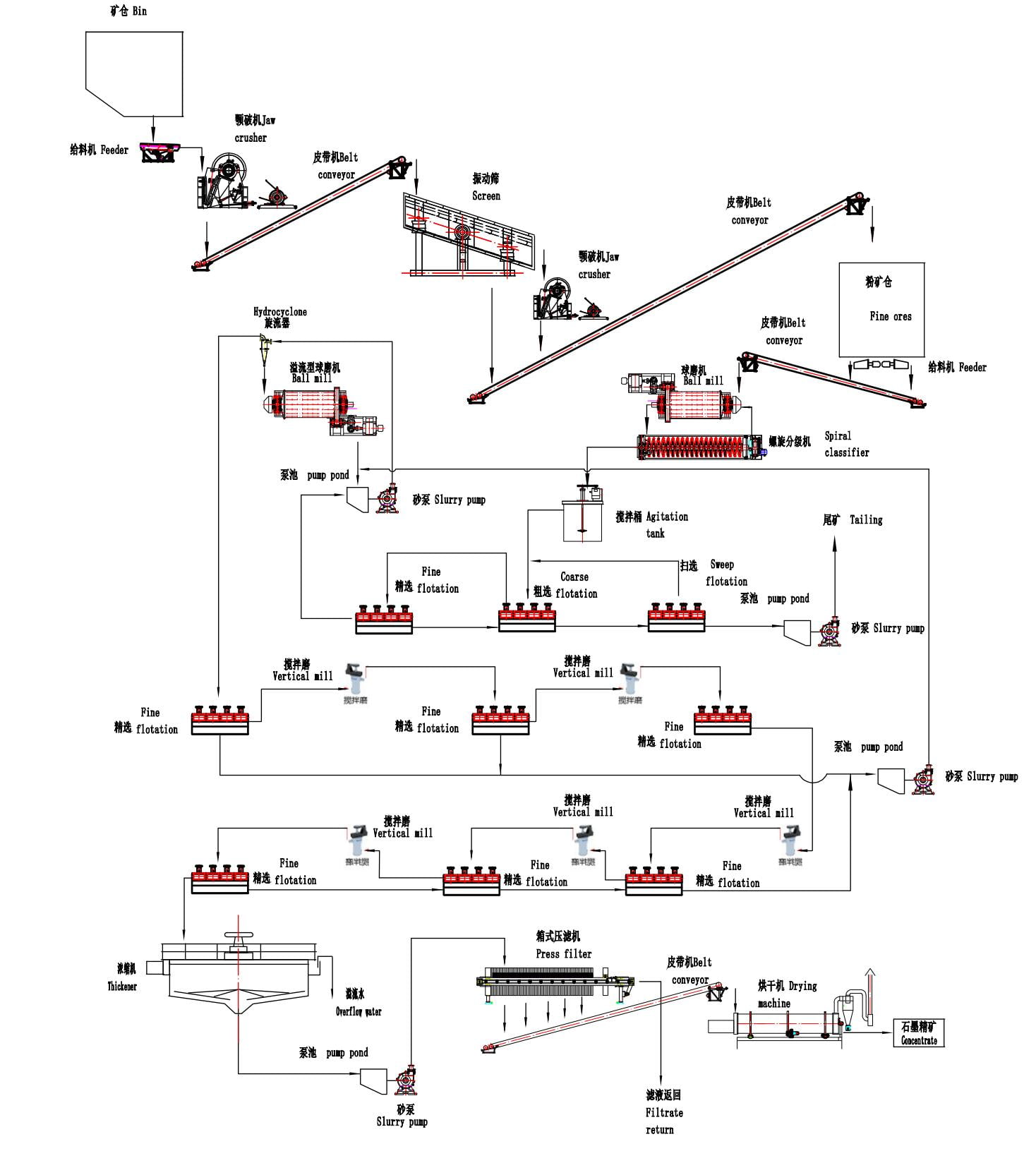
Graphite Beneficiation Process Flowsheet
- The truck/excavator unloads the raw stone into the hopper, the stone enters the vibrating feeder from the lower part of the hopper;
- The vibrating feeder feeds the stones evenly to the primary jaw crusher;
- The crushed output materials from the primary jaw crusher will be transported to a two-layer vibrating screen;
- The smaller fine size goes to the belt conveyor directly, the bigger gravel size goes to the secondary jaw crusher. The output from the secondary jaw crusher will be transported to the fine ores hopper by belt conveyor.
- The fine ores hopper is a buffering function also, under fine ores hopper use an electromagnetic vibration feeder to feed the fine ores to the belt conveyor evenly.
- The belt conveyor transports the fine ores to the ball mill for grinding.
- All the output from the ball mill goes to the spiral classifier, which is for classifying, to control the output can be less than 0.074mm( 200mesh)as much as possible.
- The output of the smaller ones from the spiral classifier goes to the agitation tank. The bigger particles back to the grinding mill again.
- After mixing from the agitation tank, will go to the first stage flotation, which including coarse flotation, fine flotation, and sweep flotation. The tailing of the first stage will go to a pump pond and transfer away by a slurry pump.
- The concentrates from the flotation will go to the pump pond and pump to hydrocyclone via a slurry pump.
- The underflow of hydrocyclone goes to second stage ball mill to grind them into small fine again, to better release the inside ore. the output goes back to hydrocyclone.
- The overflow of hydro cyclone goes to second stage flotation( including 6 times fine flotation).
- The tailings from the 6 times fine flotation go back to second stage grinding, which forms a closed circuit.
- The concentrates from the flotation go-to thickener directly, the slurry ore after precipitation, will go to a pump pond and pump to filter press via a slurry pump.
- Concentrate after filtration will go to the drying machine and then get the dry graphite concentrates.
Combined gravity and flotation beneficiation Process
For graphite ore with multiple gangues, our mining engineers suggest a combined process of gravity separation and flotation for graphite beneficiation. First, the light and heavy minerals are separated by gravity separation, and after separation, the flotation method is used to flotate the tailings, that is, the light minerals. In addition to the above-mentioned ore dressing equipment, the gravity separation and flotation combined method also uses gravity separation equipment, jigs, beneficiation shakers, and spiral chutes. One or more types of gravity separation are selected according to the properties of the graphite beneficiation equipment.