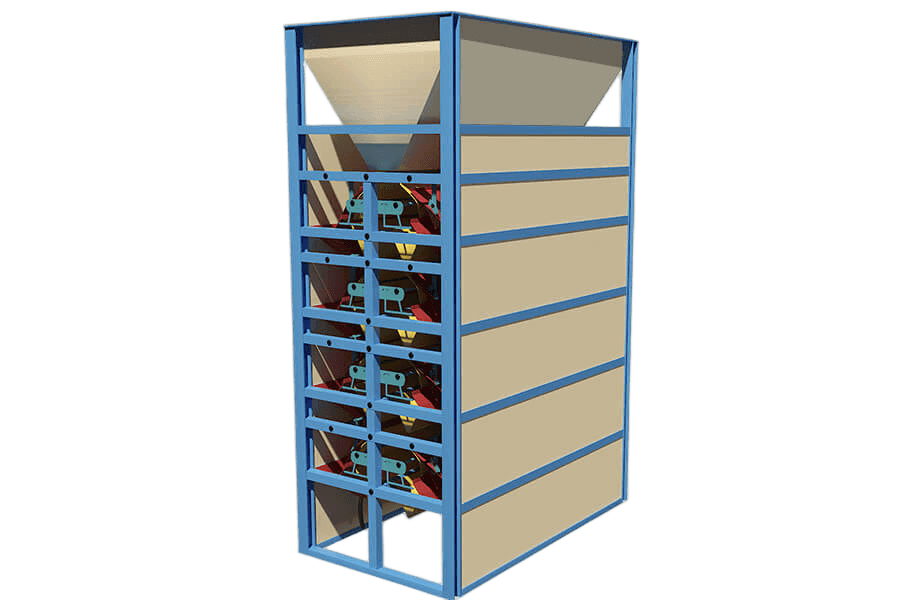
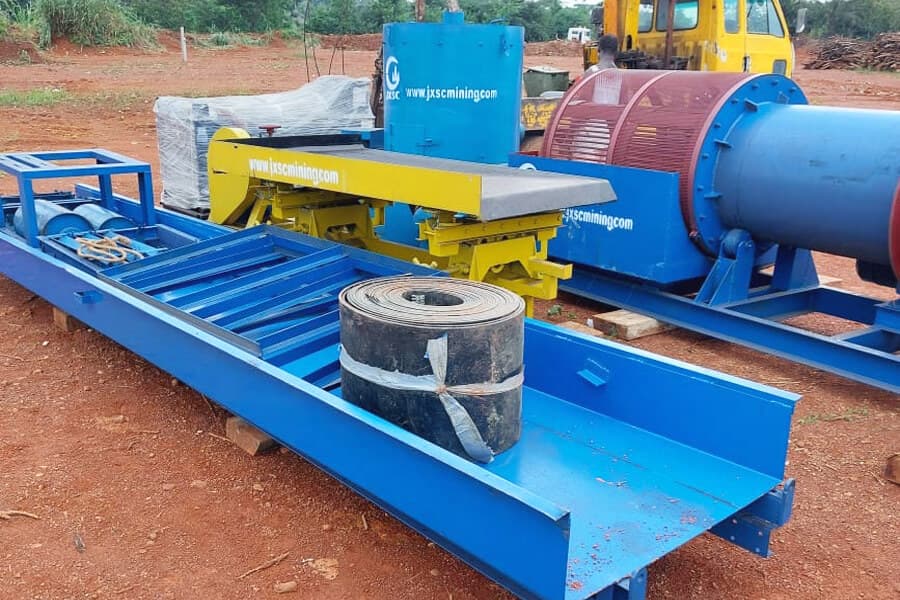
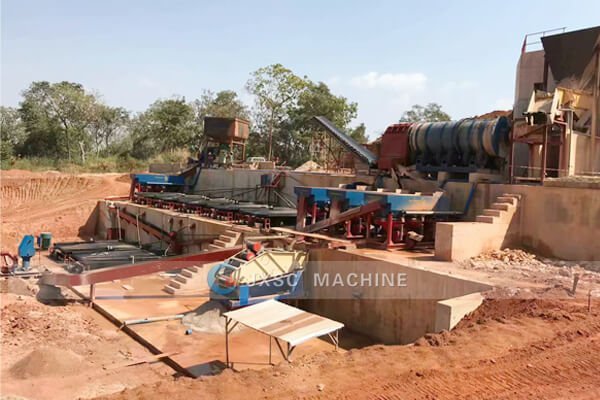
Electrostatic Separator
Capacity: 1-3T/H
Feeding: 0-3mm
Application: magnetite, ilmenite, rutile, monazite, zircon, tungsten, tinstone, zirconite, andalusite, rutile, etc
product display
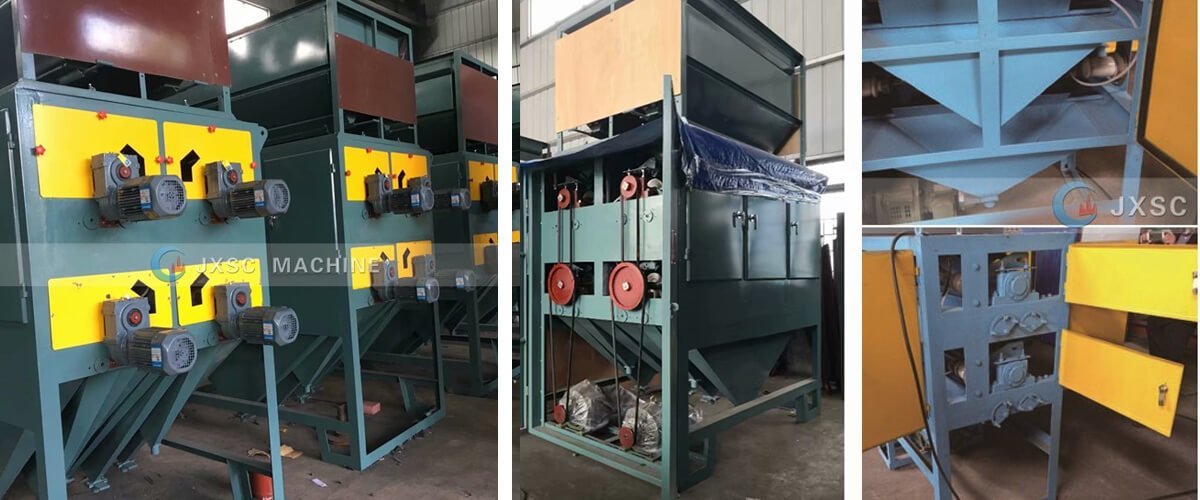

Overview
Introduction: Electrostatic separation is a physical beneficiation method that utilizes the different electrical properties of various minerals and materials for separation. A drum-type and ARC-type electrostatic separation machine is commonly used electrical separation equipment. The most suitable granularity of the selected materials for the drum-type electric separator is 0.1-1mm. The selected materials need to be dried.
Advantages Of Electrostatic Separator
- Adopt a unique feeding method, or use a separate frequency conversion speed control to control the feeding, so that the materials can evenly enter the corona electric field, and the material sorting effect can be achieved efficiently.
- JXSC electrostatic separator has low energy consumption, low noise, high output, dust-free and environmentally friendly equipment.
- The equipment runs smoothly, is safe and reliable, and the minerals after electrical separation are of higher purity.
Work principle of electrostatic separator
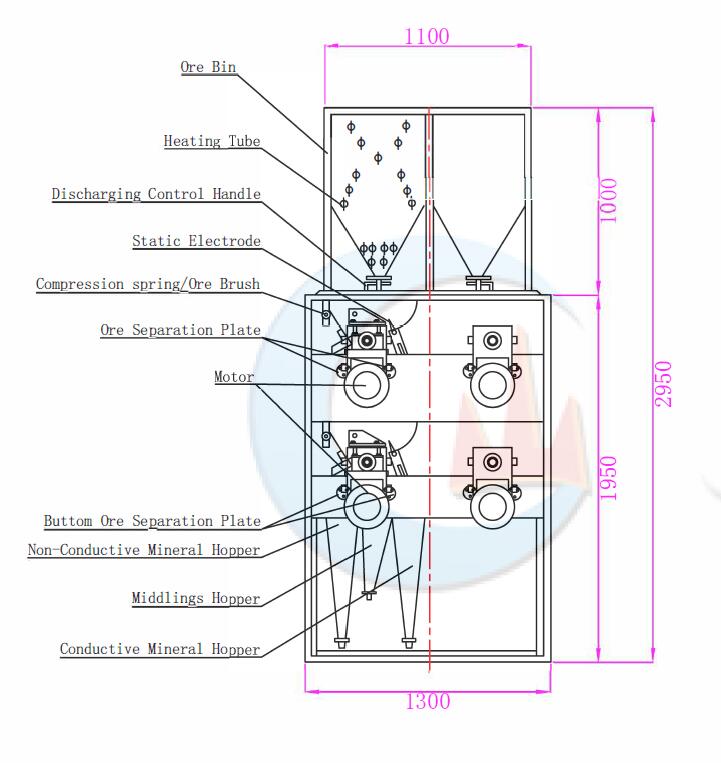
The ARC type electrostatic separator machine has the structure of two rows and four stories in each row. Each floor has an earthing curved slide board (stainless steel). On the top, it has an arc-shaped high-voltage electrostatic plate (aluminum), which is stationary (but adjustable). When connected to high voltage static electricity, the ore minerals slip into high-voltage field area via earthing arc plate, then conductive minerals charged by induction and attracted to the electrode. Due to gravity, it is discharged from the front which is different from the non-conductive ore. Meanwhile, the electric field has also affected the other ion-conductive mineral but will not be attracted into the lower re-sorting. The process will be conducted four times until the minerals are qualified.
models & specifications
|
Model |
BXJ-2A4-30 |
BXJ-2A5-60 |
|
Capacity |
1-2T/H |
1-3T/H |
|
Feeding size |
0.1-3mm |
0.1-3mm |
|
Feeding speed |
10-15cm/s |
10-15cm/s |
|
Arc-Plate size |
1600 |
1600 |
|
power consumption |
125W |
|
|
Operation voltage |
0-60KV |
0-60KV |
|
High voltage current |
0-10MA |
0-10MA |
|
machine weight |
1688KG |
2100KG |
|
Overall size |
2.1*1.6*2.3 |
2.1*1.6*2.5 |
At present, electrical selection is widely used in the following areas:
1. Sorting of non-ferrous and rare metal minerals
These two types of minerals are often firstly subjected to gravity separation or other beneficiation methods to remove a large amount of gangue minerals or surrounding rocks to obtain a certain grade of coarse concentrate, which is then selected by electric separation or in combination with magnetic separation to make useful minerals are separated from each other.
Such as the separation of white tungsten and cassiterite;
After the gravity sorting of seashore ore or land sand ore, different heavy minerals such as magnetite, ilmenite, rutile, monazite, zircon, and phosphorite are sorted;
Separation of tantalum-niobium ore and garnet, tourmaline, quartz, feldspar, mica, etc.
2. Sorting of ferrous metal ore
A small number of iron ore, manganese ore and chromium ore directly use electrical separation, most of which are only used in the concentrating process. Electric separation has a special effect on the removal of silicate minerals (such as quartz, etc.) from iron concentrate, manganese ore and chrome ore.
After the separation of these ores, an additional stage of electrical separation is carried out for beneficiation, which not only can further improve the grade of concentrates, but also greatly reduce the content of silica, which will reduce the coke ratio in iron making, save energy, and improve the blast furnace.
3. Selection of placer gold
Placer gold is also gravity separated to obtain heavy minerals, usually including gold, magnetite, ilmenite, and a small amount of quartz, etc. This heavy mineral is combined with magnetic separation and electrical separation for selection. When magnetic separation is used to remove magnetic minerals, and then electrical separation is used to select gold, gold concentrate with high grade and high enrichment ratio can be obtained, which is much superior to the general beneficiation method or mercury mixing method.
4. Sorting of non-metallic minerals
Such minerals include graphite, asbestos, diamond, apatite, coal, potassium salts, quartz and feldspar.
5. Classification of various solid materials
Including all kinds of metals and non-metals and other solid materials, in industrially developed countries, the particle size requirements of chemical raw materials, coatings, metal powders and corundum powders in metallurgy are very strict, when these materials can not use the wet classification method, electric classification has become the most feasible method, and can overcome a series of difficulties caused by wet classification and save the necessary series of concentration, filtration and drying equipment.
6. Recovery of non-ferrous metals from various solid materials or waste materials
Recovery of non-ferrous metals from various types of cutting waste and plastics; recovery of coal and spherical particles and fly ash of aluminosilicate produced in combustion from coal-fired power plants and other chimney ash.
Contact Us Now
Please fill out the information below for the quotation price and engineer’s help. We will reply ASAP!
Notice:
- We do not provide jobs and have no interest in investment or partnerships.
- We provide mineral processing equipment and solutions; not buy and sell mineral /ore /materials.
- We value your privacy and keep your information safe.