Copper exists in nature mainly in the form of sulfide ores and oxide ores, of which sulfide ores are the most important, while the slow oxidation and metamorphism of sulfide ores generate oxide ores. Among them, oxidized copper ore refers to copper ore with an oxidation rate greater than 30%. It is generally located in the oxidation zone above the ore bed, which has extremely complex physical and chemical conditions, and its mineral composition and structural structure are relatively complex. Oxidized copper ore can be used as a raw material for producing copper salts and is used to make pigments, mordants, and catalysts. It is also often used as an additive for anti-corrosion coatings to improve rust and corrosion resistance. However, with the decline in ore grades and the increase in mining costs, the beneficiation of copper oxide ores plays a key role in meeting the growing global demand for high-quality copper.
What is copper oxide ore?
Copper oxide is an inorganic substance, a black oxide of copper. The most common copper oxide minerals are malachite and azurite, followed by chrysocolla and cuprite, and sometimes copper sulfate and other soluble salts are also encountered. The oxide structure is loose and fragile, with a high content of bound copper, uneven embedded particle size, high water and mud content, and multiple components.

Copper oxide ore beneficiation methods
It is difficult to achieve the requirements of copper oxide ore beneficiation using conventional magnetic separation and gravity separation methods. However, copper oxide ore beneficiation usually involves methods such as flotation, leaching and hydrometallurgical processes, each of which aims to maximize the recovery of valuable copper while minimizing the impact on the environment. Among them, flotation is the most common and highly used method.
1. Leaching methods
Leaching is the treatment of copper oxide with an acid solution to dissolve the copper content. It has become a mainstream method in modern mining operations due to its ability to effectively process low-grade ores. The acid solution dissolves the copper oxide, which can be more easily extracted and recovered through solvent extraction techniques or electrolysis.
2. Flotation process
By utilizing more efficient reagents and optimizing the pH in the flotation machines, miners can separate copper oxide from gangue material with unprecedented accuracy, thereby increasing overall copper production. In addition, combining froth flotation with advanced sensor technology allows for real-time monitoring and optimization of parameters, paving the way for smarter, greener operations that reduce waste and energy consumption.
- Use collectors that specifically target copper oxide, such as fatty acids or sulfonates. These collectors work by modifying surface properties at the molecular level, enhancing hydrophobicity while reducing unwanted interactions with gangue minerals. The strategic application of these agents can improve separation efficiency and concentrate grade, even when challenging ores laden with impurities.
- Biosurfactants are naturally occurring compounds that enhance the separation process by altering the surface properties of copper minerals. These environmentally friendly agents can improve selectivity and thus increase the grade of the concentrate.
copper Oxide ore beneficiation plant
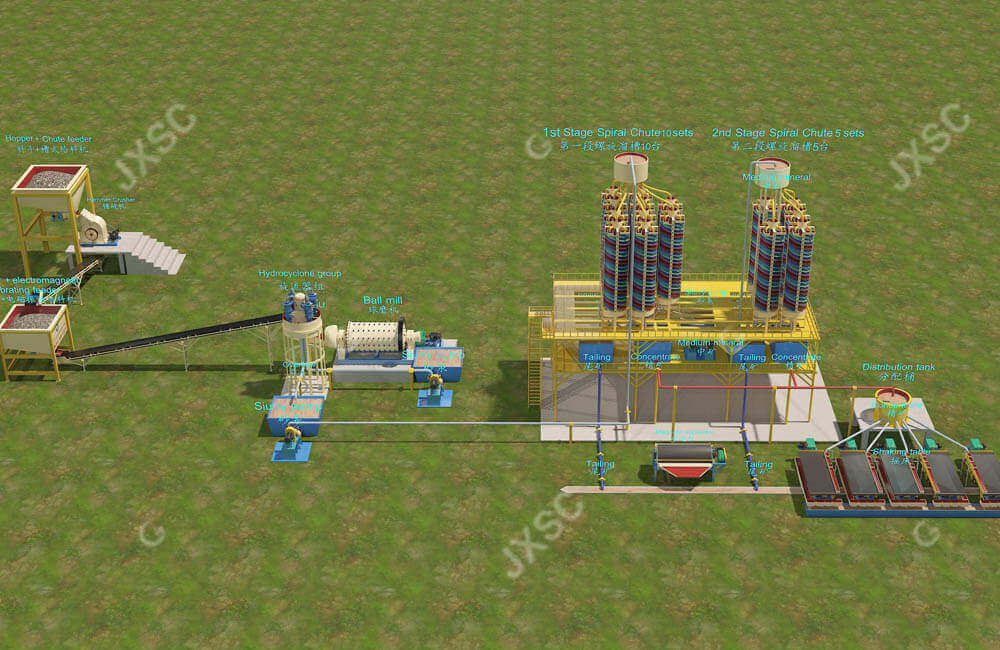
30TPH Copper Oxide Beneficiation Methods
This setup is a 30 tph rock copper oxide ore process plant . It is configured with a hopper , feeder chute , hammer crusher , conveyors ,fine ore bin, Electromagnetic vibrating feeder ,ball mill , hydrocyclone , slurry pump , spiral chute , shaking table and magnetic separator .
- The loader feeds the -350mm raw material copper ore to the hopper . The feeder chute will feed the hammer crusher uniformly . The material will be crushed till 25mm by the hammer crusher.
- The 0-25mm output will be transferred to a middle silo by conveyors . And then the electromagnetic vibrating feeder under the silo will feed 0-25mm material to the ball mill to grind till 0-1mm by conveyor .
- The 0-1 mm output will flow to one pool and then it will be pumped to hydrocyclone to separate . The overflow (around 0-0.2mm material ) will be pumped to the first 10 pcs spiral chute to separate . The underflow of the hydrocyclone will be pumped to the ball mill to grind again .
- The concentrate of the 10 pcs spiral chutes will flow to the 5 shaking table to separate again . And the middling will be pumped to the other 5 pcs spiral chute to separate . The concentrate of the 5 pcs spiral chute will be sent to the 5 shaking table to separate again .
- The concentrate of the shaking table will be sent to the magnetic separator to separate . The non magnetic concentrate is copper . And the tail is the magnetic metal.
Advances in copper oxide ore beneficiation methods have significantly improved recovery efficiency, paving the way for more sustainable mining practices. Each method offers unique advantages based on specific ore characteristics. The integration of its flotation technology can not only improve resource utilization, but also improve the cost-effectiveness of production. As demand for copper continues to rise, flotation beneficiation is being used to ensure a more efficient and responsible extraction of copper. JXSC supports customized copper ore beneficiation solutions and equipment to maximize recovery efficiency while increasing economic benefits.