Tantalum-niobium ore is a general term for minerals containing tantalum and niobium. There are many important tantalum-niobium minerals with industrial value, mainly niobium iron ore, tantalite or pyrochlore. Some tantalum-niobium exists as impurities in ilmenite, perovskite, rutile, cassiterite, wolframite and titanite. It is a rare metal and an important strategic resource. It has been widely used in metallurgy, atomic energy, aerospace, military industry, electronics, biology, chemistry and technology industries. The mineral composition of tantalum-niobium ore is complex, the composition is unstable, and the content of valuable components is low, so its dressing process is relatively complicated. Tantalum-niobium ore dressing is mainly carried out by combined processes such as gravity separation, flotation, and magnetic separation, so as to achieve the separation of various useful minerals.
Tantalum-niobium ore dressing process

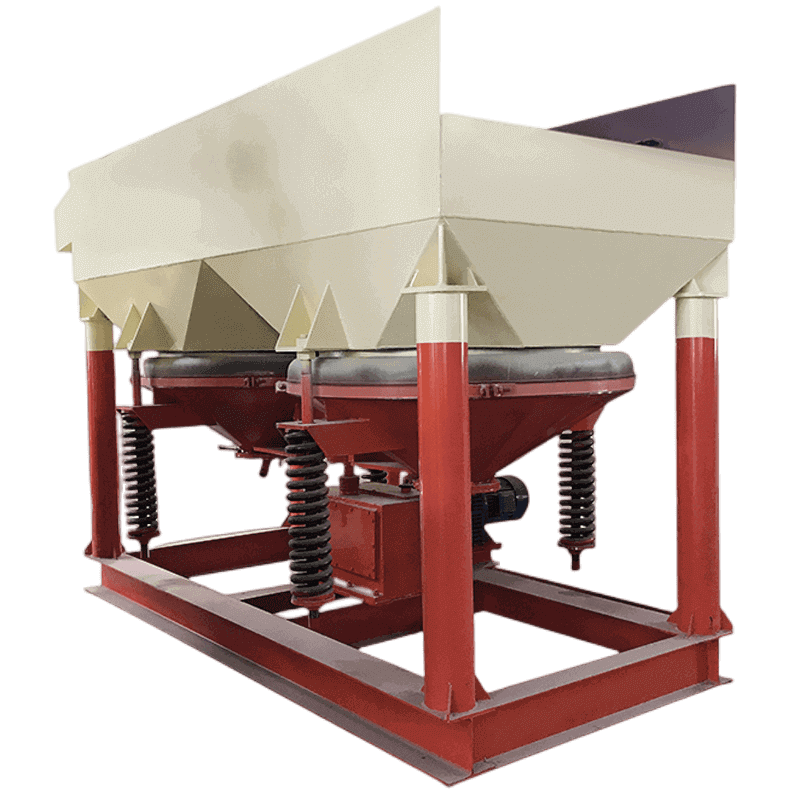
1. gravity separation
The gravity separation process for tantalum and niobium is the result of the interaction of density, particle size and mineral composition. By exploiting differences in specific gravity, this method effectively separates these metals from the surrounding gangue material, often significantly increasing recovery rates. What makes gravity separation unique in processing these critical raw materials is its environmental friendliness; it minimizes the use of chemical reagents that are harmful to health and the environment.
Innovations in device design have also revolutionized the technology. Advanced shakers and spiral concentrators increase efficiency by optimizing flow rates and angle adjustments while maximizing the accuracy of separating valuable minerals from waste.
2. Flotation
The process begins with crushing and grinding to release tantalum and niobium minerals, which are commonly found in pegmatite deposits such as coltan. Flotation takes advantage of the unique surface properties of these minerals, using specific collectors to enhance their separation from the gangue material. This selectivity improves separation efficiency by optimizing bubble-particle interactions, which maximizes recovery.
3.Magnetic separation
The process exploits the difference in magnetic susceptibility between these refractory metals to more efficiently separate them from the gangue material. Once exposed to the magnetic field produced by a powerful magnetic separator, tantalum (which is primarily paramagnetic) is largely unaffected, while niobium exhibits a stronger magnetic susceptibility. This distinction effectively separates the two elements. The innovative use of powerful electromagnets allows operators to selectively capture these valuable minerals, reducing waste and optimizing yields.
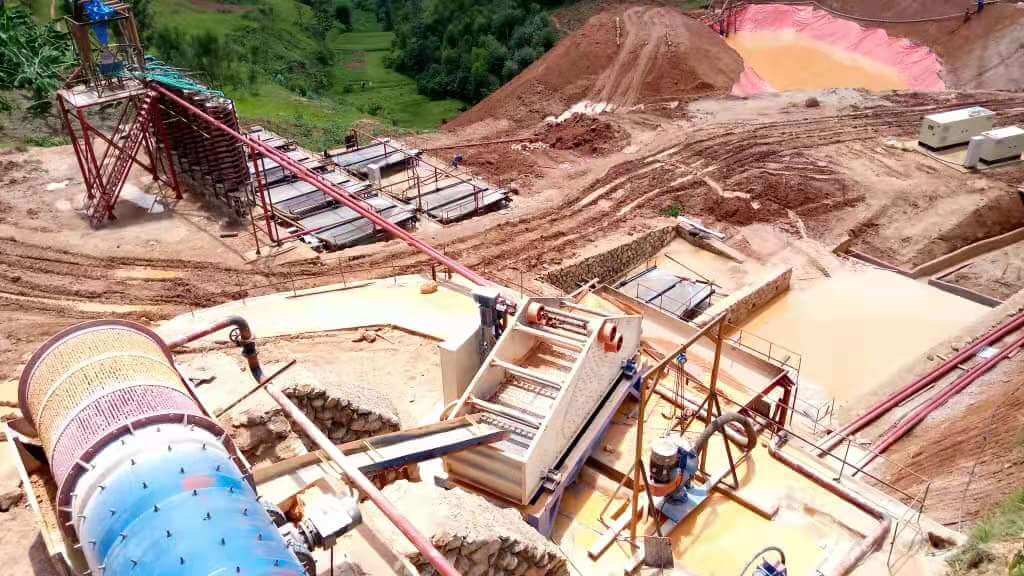
Tantalum-niobium ore dressing plant

40TPH tantalum-niobium ore dressing plant flow
This a complete 40 tph tantalum-niobium ore dressing plant, the raw material is alluvial and rock mixture type, the feeding material size is less than 120mm and there’s a lot of sticky clay in the mine.
1. Washing & centrifugal concentratorseparation
It using the trommel scrubber with a hopper. The hopper also can be made with a grizzly bar to screen the much bigger rocks. Since there’s a lot of sticky in the raw ore, here we suggest using a trommel scrubber to wash away the sticky clay. If you are raw or without too much sticky clay. You can use a trommel screen. Here the machine is with 2 layers of screen, 2 mm, and 25mm. Therefore, rocks more than 25mm will be transferred together. Then the less than 2mm materials will go to a centrifugal concentrator. The tailing from the concentrator will go to the sluice box to gather concentrate again.
2. Jig gravity separation & washing
The 2-25mm materials will go to the jig separator. The jig separator mesh size will be 2mm. Then the 0-2 mm sizes below the mesh from the jig separator and tailing from the sluice box will be sent to a spiral sand washing machine for dewatering. After that, the materials will be sent away by a conveyor belt.
3. Crushing & shaking table gravity separation
The 2-25mm materials above the mesh will be sent to a hammer crusher by belt conveyor to crush to be less than 5mm. The less than 5mm materials will go to the ball mill to grind to be 0-1 mm. After that, you need to feed the 0-1 mm materials into a shaking table to separate and collect the concentrated ore.
4. Magnetic separation
Finally, if there’re too many magnetic ores(like the magnetite, hematite, etc) inside your concentrate ores, you can dry your concentrate at first then use the 3PCS disc dry magnetic separator to remove them and get the final concentrate tantalum-niobium ores.
This capacity of plant can be customized as per request such as 10tph, 40 tph,100tph, etc. Here’s only for processing rock and alluvial mixture ore type, if your situation is different, we support customized the suitable ore dressing plant flowchart for you according to your detailed different ore situation.
Tantalum and niobium ore dressing is a complex series of separation technologies designed to maximize the recovery of these high-demand metals. Gravity separation uses the unique density difference between tantalum and niobium minerals and their surrounding materials to ensure effective separation with minimal chemical intervention. However, the more complex nature of the minerals requires the addition of combined processes such as flotation, magnetic separation or electrostatic separation for beneficiation. JXSC supports customized ore dressing plants and equipment, contact us for more details!