Magnesite is a strategic non-metallic mineral used in various industrial applications. It is mainly used in three aspects: making refractory materials, building materials, and extracting magnesium metal. Among them, refractory materials are magnesite’s most important downstream application field, accounting for more than 80% of magnesite consumption, especially in the automotive and aerospace fields. As various industries increasingly seek to transform to more environmentally friendly alternatives, magnesite has become the focus due to its wide range of applications, from refractory materials in steelmaking to advanced ceramics and environmental technologies. Improving the quality of magnesite through mineral processing can improve its market competitiveness and reduce waste by promoting the recovery of low-grade ores.
However, the magnesite flotation process is an important mineral processing method that can extract valuable magnesium carbonate from the ore. The core of the process is to use the principles of surface chemistry and selective adsorption to separate the desired minerals from unwanted impurities effectively.
What is magnesite?
Magnesite is a carbonate of magnesium, one of the sources of magnesium compounds, and can be divided into crystalline magnesite and amorphous magnesite.
In addition, magnesium compounds can also be extracted from dolomite, forsterite, brucite, magnesium-containing salt lake water, and even seawater.
Magnesite often contains iron, which results from iron or manganese replacing magnesium. It is white or light gray, shiny, with a hardness of 3.5-4.5 and a specific gravity of 2.95-3.1. It is mainly produced in Zimbabwe, Brazil, Australia and China. Its application value is mainly to produce materials with a high magnesium oxide content, which has good refractory and adhesion. In addition, it is also the main raw material used to refine magnesium metal.

Application of magnesite
The main downstream application areas of magnesite are refractory materials, chemicals, building materials, light industry and agriculture and animal husbandry. Among them, refractory materials are the most important downstream application area of magnesite, accounting for more than 80% of magnesite consumption. Common impurities are iron, calcium, manganese, cobalt and nickel magnesite. Various magnesia refractory materials are made through calcination, melting and other processes, mainly used for furnace linings in high-temperature industries such as steel, cement, glass and ceramics.
Magnesite flotation process
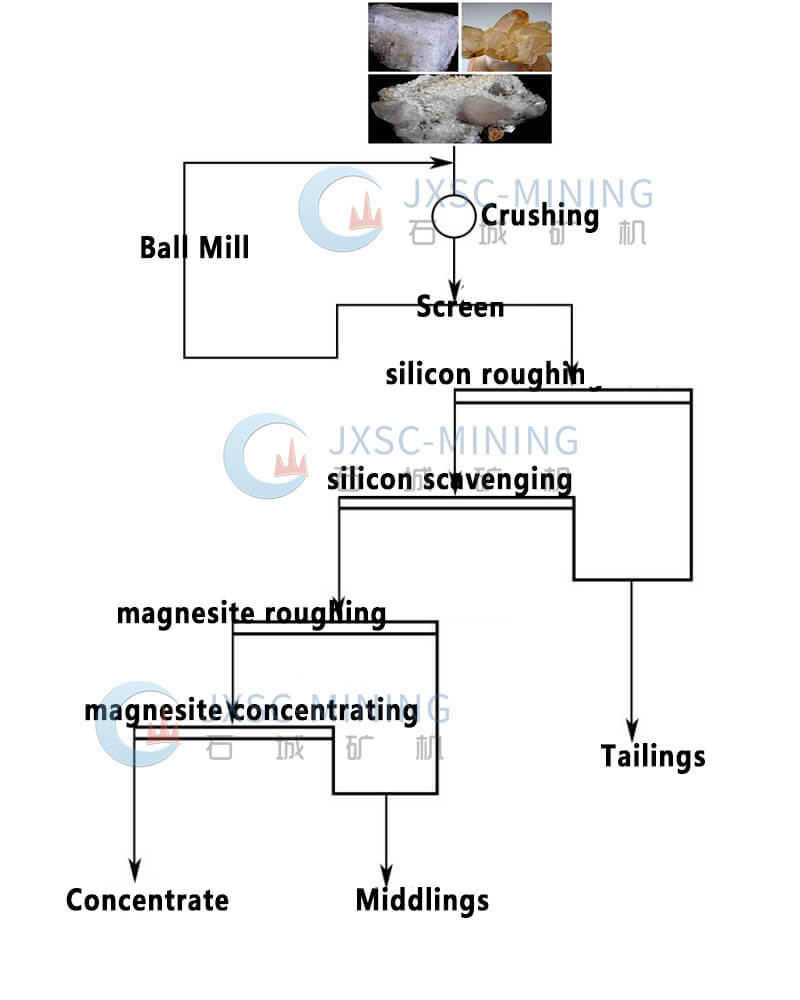
In order to remove harmful impurities and improve the crystal grade of ore, solve the separation problem of silicate gangue minerals and magnesite and magnesite and dolomite, magnesite flotation is an important purification method.
1. Crushing and screening stage
The vibrating feeder sends the raw materials of magnesite with a particle size of less than 200mm to the jaw crusher for crushing, which is then crushed to a smaller particle size by the impact crusher and enters the circular vibrating screen for screening. If the particle size of 10mm does not meet the grinding requirements, it will be re-entered into the crusher for crushing to 0-10mm.
2. Grinding and classification stage
Grinding and classification are very important for the flotation process. Grinding fineness is an essential factor affecting the sorting index. Appropriate grinding fineness can effectively dissociate the target and gangue minerals. After crushing, the ore less than 10mm enters the ball mill for monomer dissociation, and two-stage grinding or three-stage grinding is often used. The grinding particle size requirement is 200 mesh, accounting for more than 70% of the total, and the JXSC ball mill can achieve the best fineness.
3. Flotation stage
The main mineral processing equipment used in the separation stage of flotation process is flotation machine, mixing tank, and thickener. The use of a single reverse flotation process cannot effectively remove impurities in the ore, and the magnesium oxide content of the selected magnesium concentrate is still as high as 0.35%. Therefore, the magnesium ore flotation process is generally composed of reverse flotation (one coarse and one sweep) and direct flotation (-coarse-fine). Reverse flotation selects all tailings; direct flotation obtains magnesium concentrate and middlings. Magnesite is ground into magnesite powder by a ball mill, and is sent to a mixer to mix with flotation reagents, and then flotation and reverse flotation are carried out. In the thickener, the mineral particles in the slurry form flocs to reduce the water content.

4. Drying stage
The water content of magnesium ore after flotation is very high. After concentration, the water content is reduced, but it cannot be used for industrial use. Therefore, a dryer is required to completely dry the magnesium powder. Different processes are adjusted according to the specific conditions of the ore to achieve the optimal quality of the finished magnesium metal product.
Common challenges in magnesite flotation
The presence of gangue minerals
Examples include talc and ferromagnesium silicates. These impurities can significantly reduce the purity of the final magnesite product, thereby reducing its market value. Flotation mainly utilizes the differences in surface physical and chemical properties of magnesite and gangue minerals for separation. Generally, reverse flotation and forward flotation are used alternately: that is, an amine collector is first used to reverse flotation siliceous minerals; then a fatty acid collector is used for forward flotation of magnesite.
Magnesite flotation is a complex mineral processing method that utilizes the differences in the surface properties of minerals. The core of this technology is to selectively separate magnesite from other related minerals by controlling the pH value and introducing various chemicals called collectors. Flotation technology can increase the recovery rate and improve the final product’s quality by selectively separating undesirable minerals. JXSC supports customized mineral processing solutions and equipment. Contact us for more details!