Whether it’s a small-scale 50TPD gold beneficiation or a large-scale project exceeding 500 tons, designing a gold processing plant layout that achieves high recovery and low energy consumption, tailored to ore characteristics, site conditions, and investment budget, remains a core challenge for mining investors and engineers. The key to this issue often lies within the initial design plan. This article will analyze the key design elements for small to large-scale rock gold beneficiation plants, optimizing layouts from the crushing stage to final separation, providing comprehensive solutions for mines.
Small and medium-sized rock gold beneficiation plants are suitable for gold extraction using gravity separation/mercury amalgamation, offering low investment and rapid returns. Budget-savvy individuals can opt for flotation to comprehensively recover valuable metals. Large-scale processing plants should adopt CIP or CIL processes, coupled with automated control systems to increase recovery rates to over 90%. JXSC offers customized design services, covering the entire process from ore testing to environmental compliance.
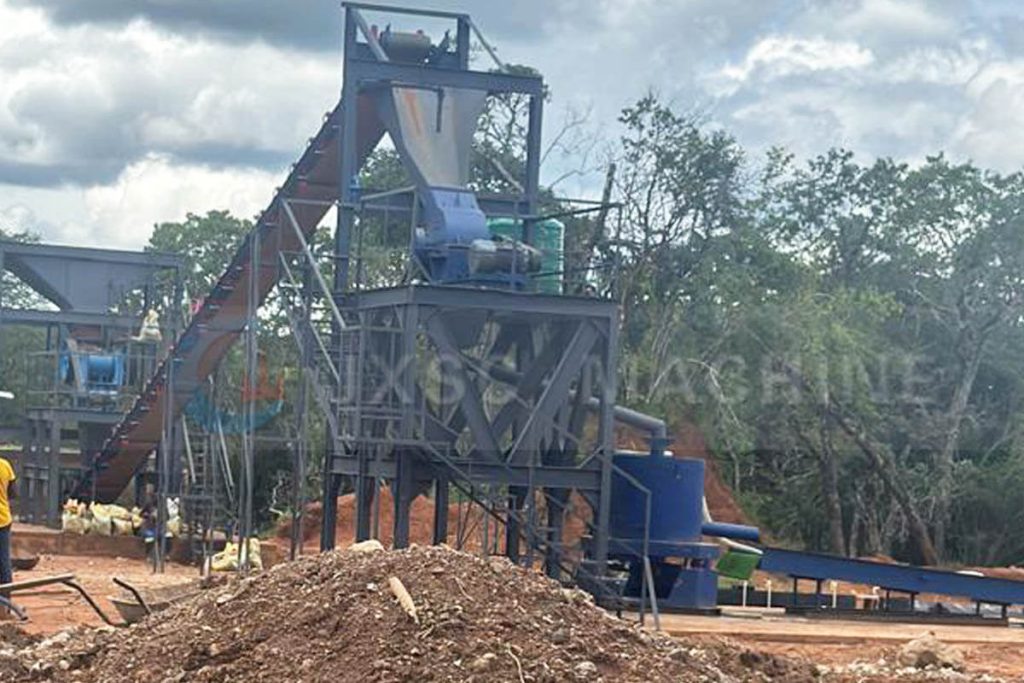

Core Elements of Rock Gold Beneficiation Design
Key Pre-Design Assessments
1. Ore Property Analysis:
Gold grade directly influences process selection. High-grade ores are typically treated with direct cyanidation, while low-grade ores require pre-concentration with gravity separation or flotation.
Fine-grained disseminated ores (<0.01mm) require more refined grinding, classification, and flotation processes. Coarse-grained ores (>0.5mm) are preferred for gravity separation.
2. Processing Capacity
- Small-scale rock gold beneficiation plants (<100 TPD) are designed for low cost, easy maintenance, and rapid commissioning. They are primarily used in small gold mines in remote areas and pilot projects.
- Medium-scale rock gold beneficiation plants (100-500 TPD) are designed to balance capacity and energy consumption, with modular expansion. They are primarily suitable for regional gold mines and renovation and expansion projects.
- Large-scale rock gold beneficiation plants (>500 TPD) focus on intelligent control, high automation, and environmental compliance. They are commonly used by large gold mining complexes and multinational mining groups.
3. Site Selection
Regarding topography, sites with a natural slope greater than 5° are preferred to utilize gravity flow and save pumping energy. Regarding water resources, the beneficiation plant consumes up to 2-5 cubic meters of water per ton of ore, requiring a long-term, stable water supply. Power supply must be compatible with peak loads (large-scale plants typically require a dedicated power line of 10kV or higher).
Small vs. Large Rock Gold Beneficiation Plant Design
Small Rock Gold Plants Design
Small to medium-sized rock gold processing lines utilize a compact L-shaped or linear layout, primarily favoring compact modular equipment to reduce material transportation distances. For example, the crushing and ball mills can be directly connected, with materials transferred directly via belt conveyors. We can also design mobile gold beneficiation equipment according to requirements, and they are suitable for projects with stable ore properties. The process flow is typically simplified to “two-stage crushing + one-stage grinding + single separation” (e.g., crushing → grinding → gravity separation/flotation process). For budgetary constraints, a combination of a jaw crusher, hammer crusher, or wet mill, followed by gravity separation equipment, can be used.
Small plants typically operate within three to four main operating sections, equipped with basic PLC control and relying on manual inspections, which better meet design requirements and costs.
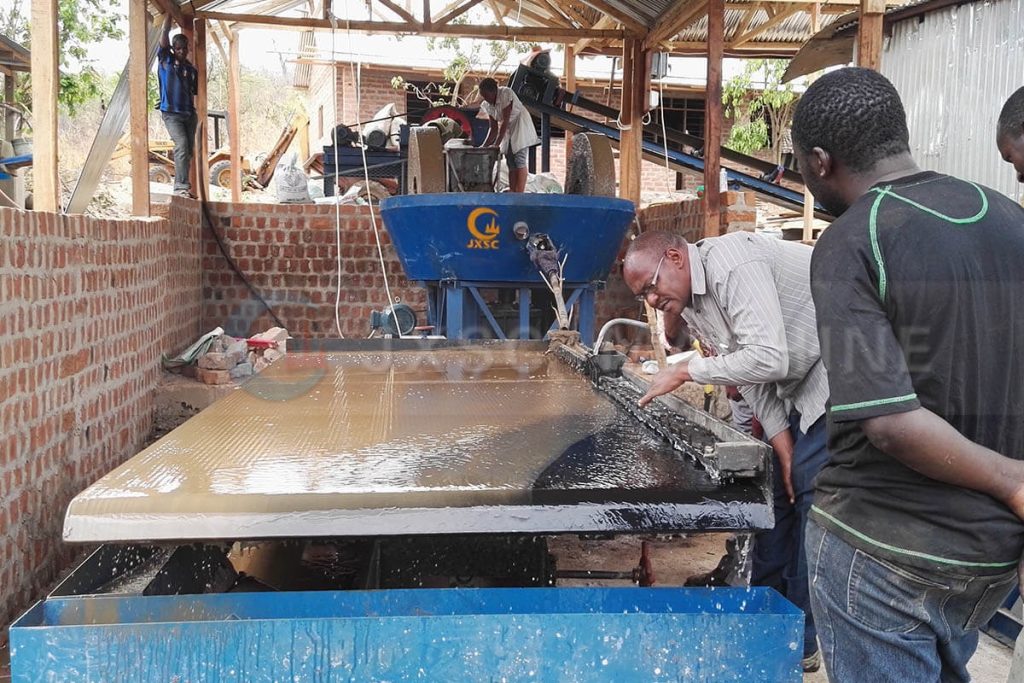

Large-Scale Rock Gold Plants Design
Large-scale rock gold plants tend to utilize customized, heavy equipment, with separate crushing, grinding, sorting, and tailings treatment areas. These typically utilize a comprehensive process consisting of three crushing stages, two closed-circuit grinding stages, and multi-stage sorting. Pre-screening is added to the crushing stage, spiral classifiers or hydrocyclones are introduced in the ball mill stage, and the sorting stage combines flotation, gravity separation, and cyanidation. Environmental protection facilities must be designed in tandem with the main plant, such as wastewater recirculation systems located below the sorting area and dust collection devices embedded directly on top of the crushing plant.
However, modern large-scale gold beneficiation plants have widely adopted intelligent control systems for gold mining equipment, such as online X-ray fluorescence analyzers for real-time monitoring of slurry grade and automated adjustments to reagent dosages through expert systems.
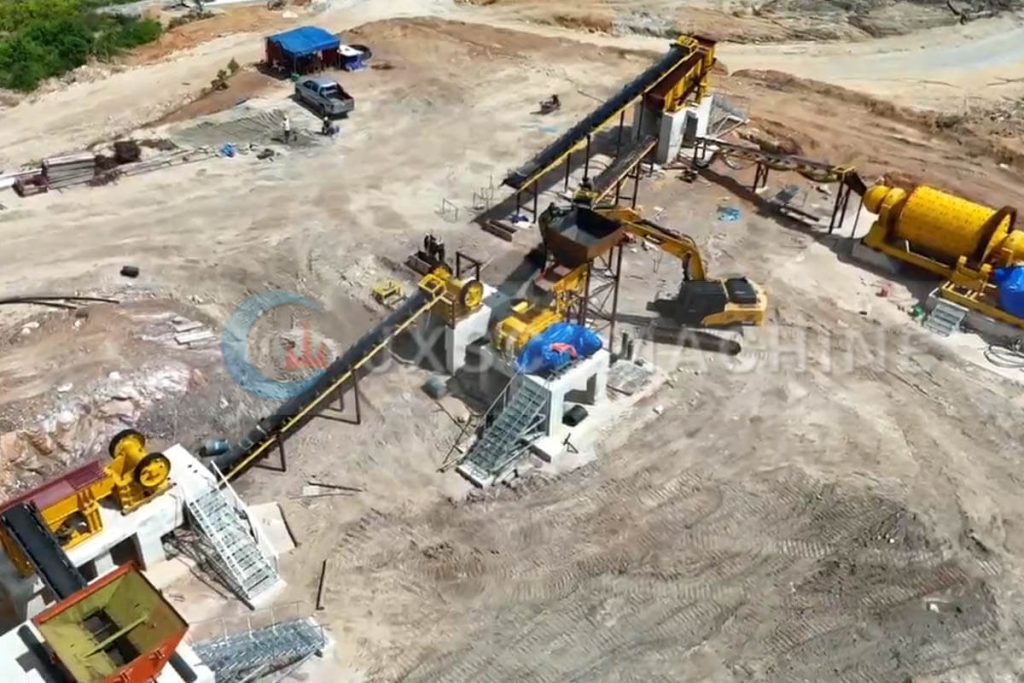

Small-large rock gold beneficiation layout and process
The specific small to large-scale rock gold beneficiation process needs to be flexibly combined according to the characteristics of the ore and the processing capacity, and the core mainly covers crushing, grinding, and sorting. Common processes include crushing, grinding, gravity separation, flotation process, CIP, CIL, and cyanide leaching, concentration, and tailings processing.
20TPH rock gold gravity beneficiation plant
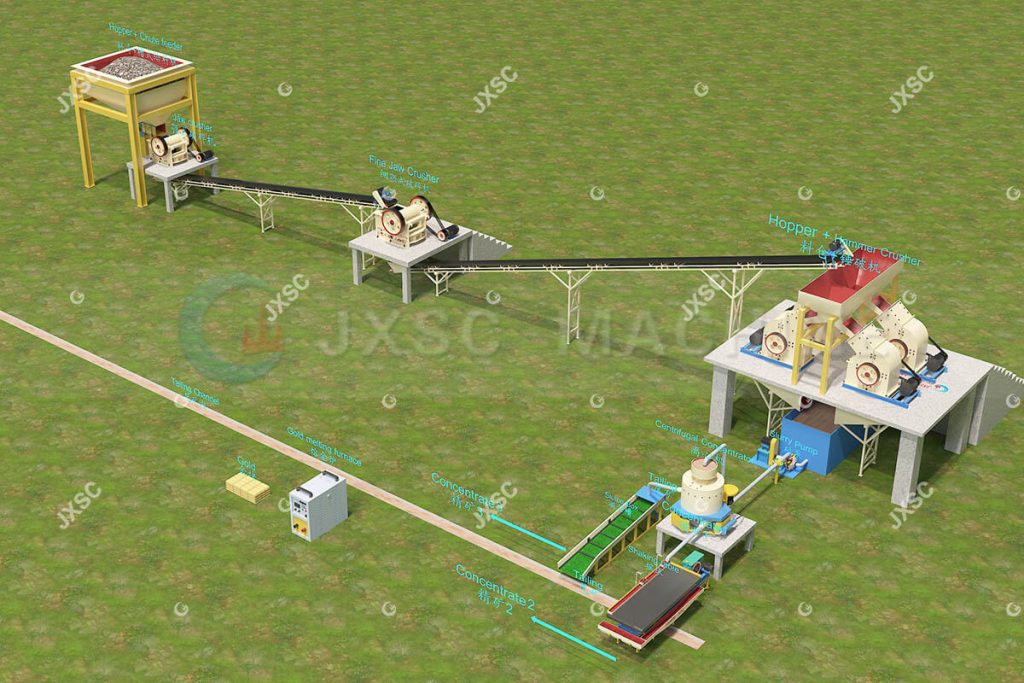

- The coarse jaw crusher crushes the big stone size to less than 100mm, and the output will be transported to the fine jaw crusher via a belt conveyor.
- The first crushed materials go to the fine jaw crusher. The fine jaw crusher crushes the materials to be fine less than 30 mm.
- The materials less than 30mm enter into the transfer bin, then go to the hammer crushers to be crushed at a range of 0-2mm.
- And then, the materials go to the gold centrifugal concentrator for the first separation.
- Tailings of the centrifugal concentrator go to sluice box for recovering more gold. Then the sluice box concentrates are sent to the shaking table for concentrating gold.
150TPH Rock Crushing Plant & 50TPH Rock Gold Beneficiation Plant
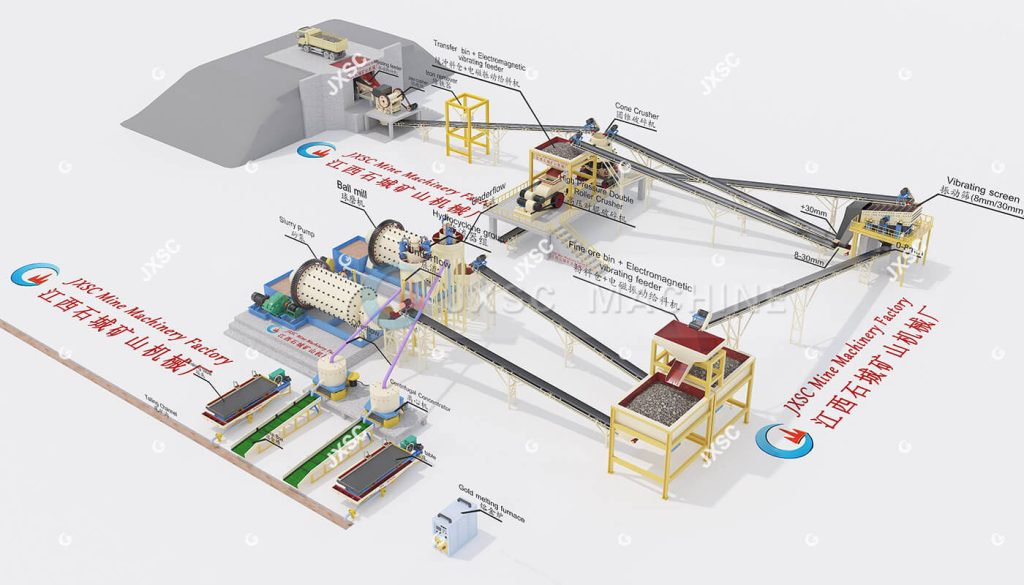
- First, the raw ore falls into the raw material feeding hopper and is conveyed by the belt conveyor to the jaw crusher and cone crusher for primary and secondary crushing.
- The crushed ore goes through a vibration screen: the +30mm part is returned for re-crushing, while the 0 – 8mm and 8 – 30mm parts move to the next steps. The 8 – 30mm ore is crushed by the high-pressure double roller crusher, then mixed with the 0 – 8mm ore and sent to the hydrocyclone and ball mill (not shown) for grinding and classification.
- The fine ore enters the centrifugal concentrators and shaking tables for gravity separation to recover gold. Finally, the concentrate is smelted into gold blocks in the gold smelting furnace, and the tailings are discharged.
600TPD( 25 TPH) Rock Gold CIP Plant
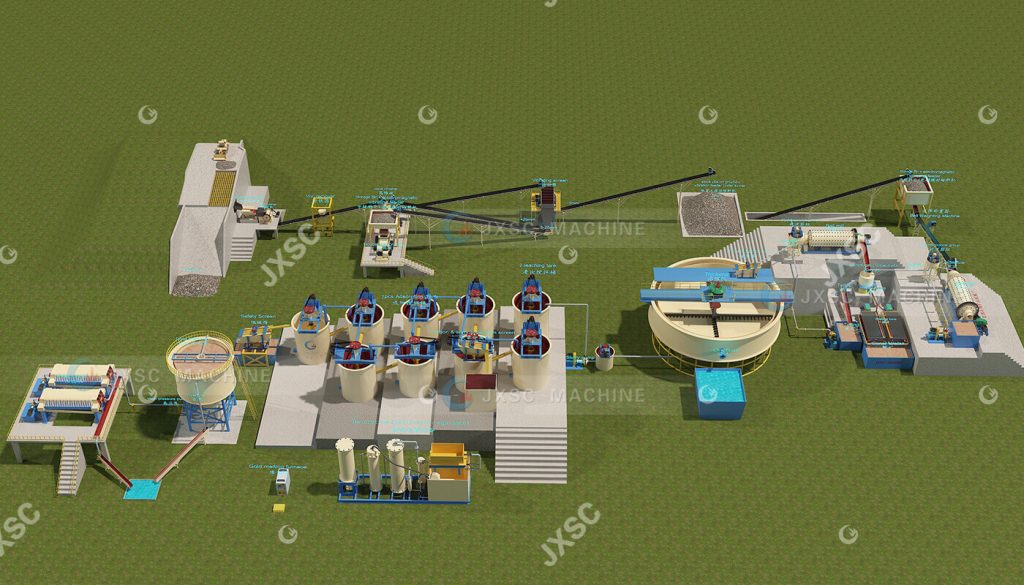

1. Feeding and Crushing System
Process: A vibrating feeder evenly feeds raw ore <500mm into a three-stage crushing system (jaw crusher, cone crusher, roller crusher), where it is finally crushed to 0-5mm particles and sent to the stockpile.
2. Two-Stage Ball Mill System
Process: The ball mill grinds the ore, which is then classified by a hydrocyclone. The coarse sand is returned for re-grinding, resulting in a final product particle size of 80% less than 200 mesh (0.074mm), ensuring complete dissociation of the gold minerals.
3. Gravity Concentration System
Process: The overflow from the ball mill cyclone enters a centrifugal concentrator for roughing, followed by concentrating on a shaker to obtain gold concentrate. The tailings enter a second ball mill cyclone to ensure the final particle size meets the specified standards.
4. Leaching Pretreatment
Process: After safe screening to remove impurities, the fine ore pulp enters a thickener where flocculants are added for concentration. The overflow enters a sedimentation tank for recycling, and the underflow is pumped into an agitation tank where it is added with reagents and then sent to the leaching tank.
5. Leaching and Activated Carbon Adsorption
Equipment: 8 dual-impeller adsorption agitator tanks (with Roots blower aeration) use activated carbon to adsorb gold from the slurry.
6. Gold-Loaded Carbon Desorption Electrolysis
Process: The gold-loaded carbon passes through a safety screen and enters a desorption electrolysis system at room temperature and pressure to produce gold sludge. The sludge is dried in a drying furnace and then melted into gold ingots in an alchemy furnace.
7. Tailings Water Recycling System
Process: The tailings from the adsorption tank are first screened through a linear vibrating screen to recover the carbon. The slurry below the screen is pumped into a cone tank and then filtered through a filter press. The filtrate is recycled to achieve water recovery.
Process selection must be based on ore properties (grade, embedded particle size), resource reserves, and environmental protection policies. Small rock gold plants focus on “survival,” while large rock gold plants focus on “sustainable development.” An efficient linear layout of crushing-grinding-sorting-tailings can reduce energy consumption, and automated control systems can improve recovery stability. Efficient recovery (85%-95% recovery) is achieved primarily through crushing and grinding optimization and separation process adaptation (flotation + gravity separation + CIP/ CIL/ cyanide gold extraction). JXSC advocates for customized gold mining equipment and process design, covering the entire chain from ore testing to environmental compliance, helping mines of different sizes maximize their benefits. Contact us for exclusive mineral processing plant solutions!