What complex processes does seemingly ordinary gold ore undergo to transform into glittering pure gold? Gold has been a highly valuable precious metal since ancient times. It is not only a core material for jewelry but also plays an irreplaceable role in the electronics, finance, and even aerospace industries. However, what truly makes gold ore precious after it is mined is the series of processes involved in washing and screening, crushing, grinding, extraction (gravity separation, flotation, CIP, CIL), sorting, and tailings processing, transforming rough gold ore into pure gold ingots. This article will guide you through the entire process from ore mining to final purification, helping you obtain the highest and best purity gold after ore beneficiation.
The entire process of gold ore processing to pure gold includes steps such as washing and screening, crushing and grinding, cyanide extraction, gravity separation, flotation, CIP or CIL, smelting, and tailings treatment. JXSC’s various gold beneficiation solutions balance high efficiency and environmental protection, and can be customized according to your ore, processing capacity, budget, and other needs, ultimately producing 99.99% pure gold.

1. Gold Ore Mining
Open-pit mining is suitable for gold deposits less than 100 meters deep, with large reserves and relatively low grades (such as porphyry gold deposits). It exposes the veins by stripping away the topsoil and rock, and then uses large machinery for batch excavation. It is low-cost and efficient, but occupies a large amount of land and damages the surface ecosystem. It is commonly used in large, low-grade gold deposits near the surface.
Underground mining is for vein-type gold deposits that are buried deep (over 100 meters) and have high grades. It requires drilling shafts and tunnels to reach the ore layer. It has less impact on the surface but has a high technical threshold and significant safety risks, with mining costs 2-3 times higher than open-pit mining. It is more suitable for ore bodies with complex geological conditions.
Regardless of the process, the mined ore must immediately undergo pre-processing to clear obstacles for subsequent gold ore crushing, grinding, and gold beneficiation technologies.
2. Gold Ore Pretreatment
Pretreatment is a crucial link between mining and deep processing. Its core objective is to remove waste rock, reduce impurities, and improve the targeting of subsequent processes.
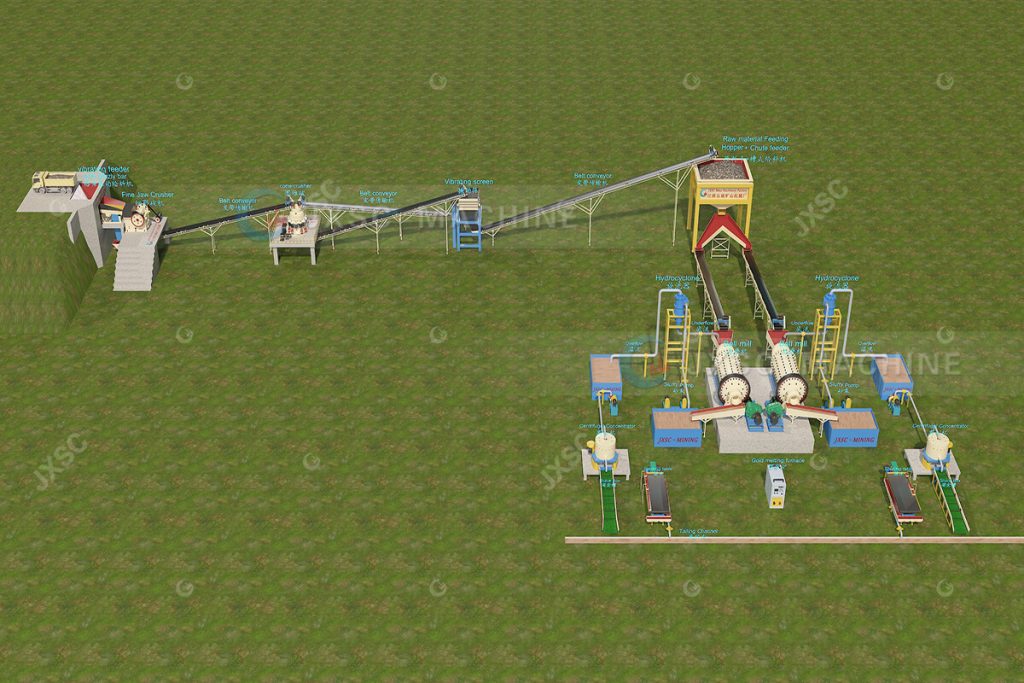
First, preliminary screening: high-grade small-sized ore is sorted manually to quickly separate waste rock; large-scale ore is graded by particle size using vibrating screens, with coarse ore >50mm fed into crushing equipment. Second, washing: Using trommel scrubbers, trommel screens, and trough washers or other ore washing equipment remove surface mud and clay from the ore, preventing clogging during subsequent crushing and grinding.
Pretreated ore has uniform particle size and reduced impurities, enabling it to efficiently enter the gold ore crushing and grinding stage. This provides fine-particle raw material for gold leaching methods (such as cyanide leaching) and lays a quality foundation for subsequent pure gold refining processes and gold ingot casting.
3. Gold Ore Crushing & Grinding
Why crush the ore?
This is because gold particles in ore are often encased in a hard quartz or other mineral matrix. Without crushing, chemical agents (such as cyanide solutions) cannot fully contact the target metal, leading to a sharp drop in extraction rate. Theoretically, the smaller the ore particles, the larger the exposed surface area for gold, and the higher the efficiency of the leaching reaction.
Crushing and Grinding Process:
This process typically employs a staged process of “graded crushing + fine grinding.” The first stage is completed by a jaw crusher, whose principle is similar to the biting action of ancient dinosaurs. Through the compression of two high-strength manganese steel plates, the raw ore is crushed to a size of about 10cm. Subsequently, secondary crushing is carried out by crushing equipment such as cone crushers, hammer crushers, or impact crushers, producing crushed stone of 2-5cm. A closed-loop system consisting of a ball mill and a spiral classifier is then used. The rotating steel balls inside the tank create a waterfall-like impact, mixing and grinding the finely crushed ore with the steel balls and water to a fine powder of approximately 200 mesh. This step fully exposes the gold particles encased in the ore, significantly improving the gold recovery rate in subsequent beneficiation processes.
4. Gold Ore Extraction Techniques (Optional)
Gold ore extraction and enrichment processes are the core of gold beneficiation technology, capable of increasing the grade of raw ore by tens of times and determining the quality of raw materials for subsequent refining.
(1) Gravity Separation
Gold has a density of 19.3 g/cm³, far exceeding that of gangue minerals such as quartz (2.6 g/cm³). Therefore, gold particles can be concentrated by settling under the action of water flow or vibration using gravity separation equipment such as jigs, shaking tables, or spiral sluices. This method is simple to operate and low in cost, especially suitable for the pretreatment of placer gold deposits or coarse-grained vein gold deposits. However, gravity separation has limited effectiveness for fine-grained gold and needs to be combined with processes such as leaching and electrolytic extraction to achieve the recovery of gold of all particle sizes.
(2) Gold Ore Flotation
The principle is to add a collector (such as xanthate) to the flotation machine or flotation column, making the surface of gold particles hydrophobic. After air is introduced to generate foam, the gold particles adhere to the foam and float to the surface. The foam is then scraped off to obtain gold-bearing concentrate. This gold flotation method can increase the grade of raw ore by 10 to 50 times and is suitable for fine-grained disseminated sulfide gold ores.
(3) Cyanide Gold Extraction Method
The principle of the gold CIP or CIL process is that after the gold ore is ground to 200 mesh, cyanide reacts with gold in a weakly alkaline environment to form a soluble gold-cyanide complex. The gold is then recovered through activated carbon adsorption or zinc powder displacement. In the CIP process, granular activated carbon is directly added to the cyanide leaching solution. The gold-cyanide complex adheres to the carbon surface through physical adsorption, and after desorption with a high-temperature sodium cyanide solution, a high-concentration gold solution is obtained. The zinc displacement method involves adding zinc powder to the gold solution, utilizing the reducing properties of zinc to displace elemental gold.
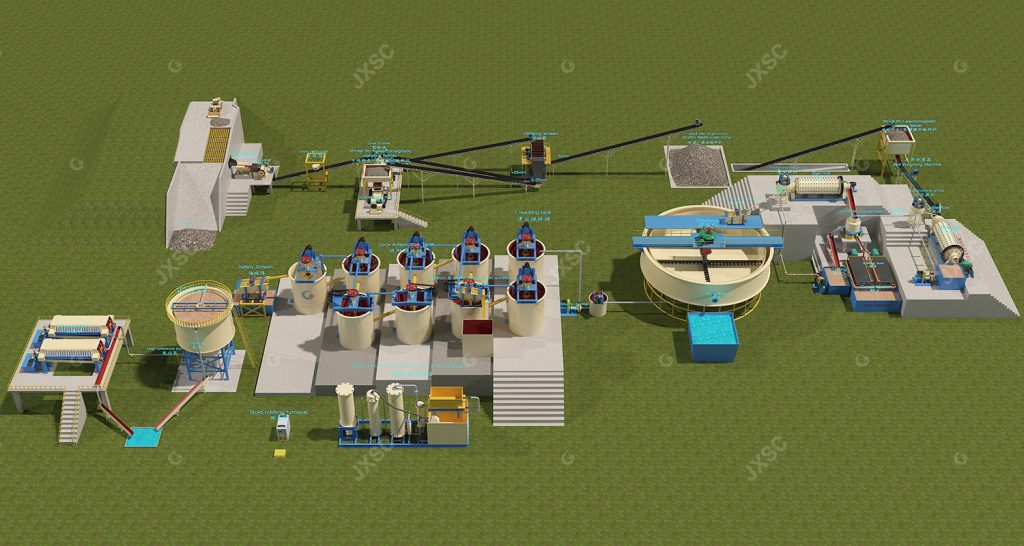
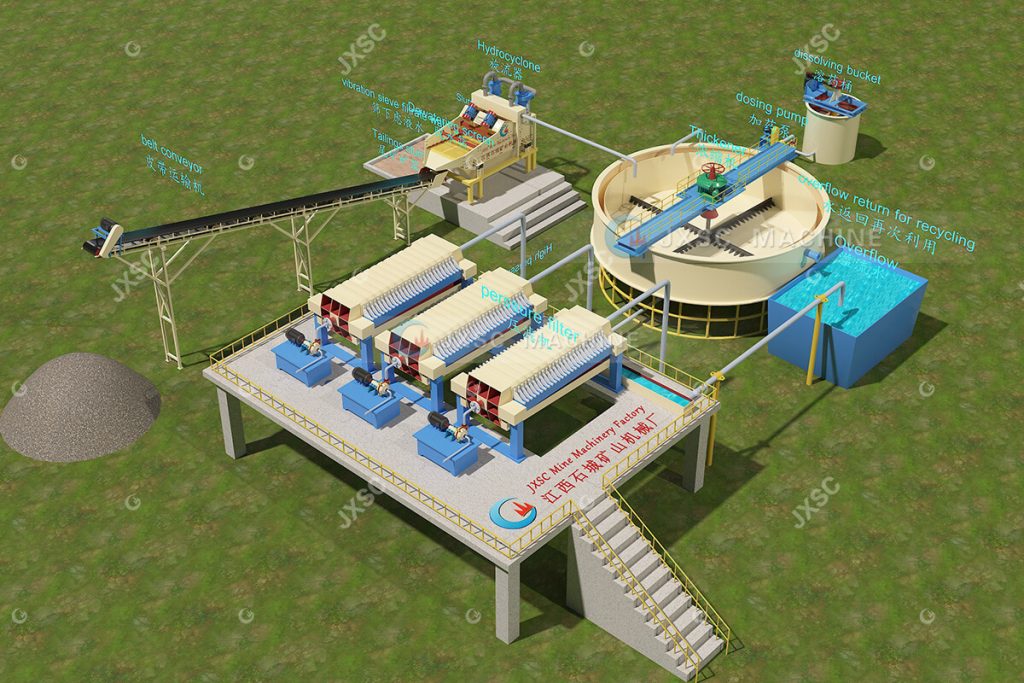
The key steps in pure gold purification mainly employ a combination of “activated carbon adsorption + electrolytic recovery.” Electrolytic refining is a crucial step in achieving high purity in pure gold production and is also the core manufacturing process for electrolytic gold. The principle is as follows: In an electrolytic cell, a coarse gold plate containing impurities (including silver, copper, etc.) is suspended at the anode, while a pure titanium or pure gold plate is used at the cathode. The electrolyte is a mixture of potassium gold cyanide and potassium hydroxide. When electricity is applied, the coarse gold at the anode dissolves into gold ions, which preferentially deposit at the cathode as dense electrolytic gold. Impurities form anode slime (containing silver and platinum group metals). This step removes impurities such as silver and copper from the gold solution and is the core of the pure gold refining process, ensuring the high purity of the final product. The recovered activated carbon can be reused, further reducing costs. It is also one of the most mature high-purity gold production technologies in the gold refining process.
This CIP/CIL processing method boasts a recovery rate of up to 95% and is suitable for processing various fine-grained gold ores. It can even handle “refractory gold” that cannot be recovered using traditional processes.
5. Gold Ore Melting and Refining
The pure gold ingot casting process involves three steps: melting, impurity removal, and casting. First, pure gold powder is placed in a medium-frequency furnace and heated to 1064℃ to melt it into a liquid. Borax is then added to remove oxide impurities, ensuring the gold’s purity. Finally, the liquid gold is poured into a standard mold (such as a 1kg gold bar mold) and cooled to form the desired shape. Finished gold products undergo polishing and laser engraving (marking purity, weight, and serial number) to ultimately obtain gold bars or ingots with a purity of 99.99%, suitable for jewelry making, investment collection, or industrial applications. This final stage determines the appearance and quality of the finished product, requiring strict control of temperature and cooling rate to avoid defects. Alternatively, it can be used as mine backfill material, promoting the comprehensive utilization of tailings and aligning with green mining standards.
6. Gold Tailings Processing
Gold tailings treatment is a crucial final stage in environmentally friendly gold mining processes, focusing on the dual core objectives of resource recovery and comprehensive utilization of tailings. Reprocessing involves technologies such as flotation and cyanide leaching to recover residual gold, silver, copper, and other valuable metals from the tailings, maximizing resource value. Alternatively, a dry tailings discharge process can be employed, using concentration, dewatering, and pressure filtration to reduce the moisture content of the tailings to below 15%, rendering them harmless and converting them into building aggregates or mine backfill materials, promoting comprehensive tailings utilization and aligning with green mining standards.
Conclusion
Gold ore processing into high-purity gold: The entire process includes core steps such as washing and screening, crushing and grinding, gravity separation, flotation, electrolytic refining, tailings treatment, etc. Need a customized gold extraction plant? We provide support for gravity separation, flotation, CIP or CIL, tailings treatment technology, and high-recovery rate gold mining equipment! Consult our experts now for a customized solution!