Ilmenite is the most important titanium ore and a major source of titanium dioxide, which is used in paints, printing inks, fabrics, plastics, paper, sunscreens, food and cosmetics. It has weak magnetic properties, and ilmenite in primary ore often coexists with magnetite and vanadium-titanium magnetite. Ilmenite in placer is often co-produced with rutile, zircon, monazite, and xenotime. Ilmenite has a wide range of uses and can be processed into titanium dioxide, various titanium-containing compounds, wear-resistant ceramic materials, magnetic materials, etc. The iron-containing waste residue can also be used to make flocculants and manganese dioxide. It can be seen that different characteristics of ilmenite ore also put forward different requirements for ilmenite beneficiation methods. Among them, the most important ilmenite beneficiation processes are gravity separation, magnetic separation, flotation and electric separation.
About Ilmenite Iron ore

Ilmenite, also spelled haematite, is a weakly magnetic iron ore with better floatability than magnetite and wide distribution. It is an oxide mineral of iron and titanium and is the main ore used to refine titanium. In nature, ilmenite resources can be divided into two categories: primary ilmenite and alluvial ilmenite according to the actual situation. Among them, primary ilmenite is mostly associated with titanomagnetite and vanadium titanomagnetite, which is characterized by large and concentrated reserves, suitable for large-scale mining, but with large gangue content, low recovery rate and poor selectivity. Alluvial ilmenite belongs to secondary ore, which is characterized by loose structure and good selectivity, but the grade of raw ore is low, and the ore is easy to slime.
Ilmenite beneficiation Process
1. Gravity separation method is suitable for coarse-grained disseminated and fine-grained aggregate disseminated ilmenite.After coarse crushing and secondary crushing, a large amount of gangue and desliming can be discarded through gravity separation equipment, such as spiral chute, shaking table, etc. Most of the small and medium-sized ilmenite beneficiation plants, the beneficiation process is mainly gravity separation, and most of them use spiral chute for beneficiation. For the ilmenite placer deposit whose mineral composition is mainly ilmenite and quartz, the beneficiation process has better effect and low beneficiation cost.
2. Magnetic separation: Ilmenite is a weak magnetic mineral, and its specific magnetic ratio and density are higher than those of gangue minerals. For minerals of the same particle size, it has a much larger volume magnetization than gangue minerals. In this way, when magnetic separation is performed under a certain field strength (electric field strength and direction), gangue minerals and a part of fine-grained iron-bearing silicate minerals in ilmenite are easily thrown into tailings. It can effectively separate ilmenite and gangue minerals to enrich titanium metal and treat ilmenite that is difficult to enrich by gravity separation. It is often used in selection, tailing and other links. Pure ilmenite is paramagnetic (very weakly attracted to magnets), but ilmenite forms a solid solution with hematite, which is weakly ferromagnetic and therefore clearly attracted to magnets. Natural deposits of ilmenite often contain intergrown or dissolved magnetite, which also contributes to its ferromagnetism.
3. Flotation separation is an efficient method to recover fine-grained ilmenite. It is used for flotation separation of primary titanium-bearing ores, especially the separation of fine-grained titanium-bearing ores, and sometimes for coarse concentrate beneficiation. Our flotation machine is an efficient method to recover fine-grained ilmenite. Before ilmenite flotation, generally, sulfide minerals are separated by flotation, and then ilmenite flotation is carried out. Sulfide ore flotation adopts conventional flotation reagent system, that is, xanthate is used as collector, pine oil is used as foaming agent, and sulfuric acid is used as pH adjuster. Some factories also use copper sulfate as activator for sulfide ore flotation.
4. Electric-separation method is mainly to deal with the coarse concentrate containing titanium pyroxene and other non-conductive impurities produced by gravity separation and magnetic separation. It is widely used in the selection process, and the electro-separation method has requirements on the particle size of ilmenite. The lower limit is 0.04mm, and pretreatments such as heating and radiation irradiation are required before electrification. This is to ensure the normal operation of the electro-separation process, avoid unnecessary situations, and improve the efficiency of mineral processing technology.
Ilmenite beneficiation Plant
The beneficiation process of ilmenite is relatively complex, involving various beneficiation methods such as gravity separation, magnetic separation, flotation, and electrical separation, so more beneficiation equipment is required. Including concentrators for classifying ore particles according to particle size, gravity separation equipment for sorting tailings, weak magnetic separators for removing strong magnetic minerals, strong magnetic separators for selecting ilmenite, flotation machine for the flotation of sulfides and fine-grained ilmenite, the electric separator of selected ilmenite, etc.
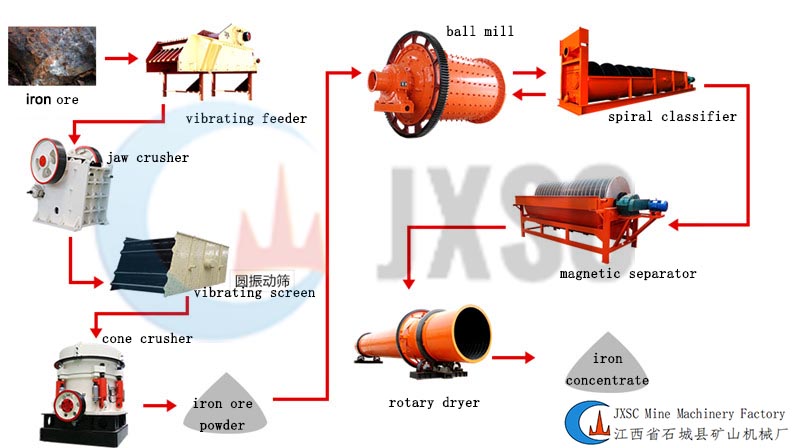
In a word, the choice of beneficiation method of ilmenite mainly depends on the properties of the material. Since the specific gravity of titanium minerals is larger than that of non-metallic gangue minerals, gravity separation can be used for pretreatment or roughing and tailing, and ilmenite with a small specific gravity of gangue minerals can also be enriched. The magnetic separation method is widely used in iron removal operations to improve the concentrate grade of ilmenite. Flotation is more suitable for beneficiation of primary ilmenite fine-grained ore. Due to the complex nature of ilmenite minerals, there are great differences in the properties of different minerals, it is necessary to determine the appropriate ore beneficiation process and equipment through beneficiation tests to ensure the beneficiation effect of actual production.