Sulfide ores are common in many parts of the world and may contain trace or large amounts of valuable elements such as copper, gold, lead, zinc, and nickel. Sulfide ores contain high concentrations of sulfur-containing minerals and metals critical for various industrial applications.
Sulfide ore beneficiation involves refining minerals with sulfur-containing compounds, such as sulfides and sulfates, and separating them into their elemental components. Its mineral processing method mainly extracts valuable metals from sulfide ores. Froth flotation is a widely used method; leaching is another effective method involving chemical or biological agents to dissolve sulfide minerals. Its flow typically involve multiple stages designed to maximize the recovery of valuable metals while minimizing environmental impact. The choice of beneficiation method depends on various factors such as ore type, mineralogy, and desired results. This article will provide an overview of sulfide ore types, beneficiation methods, the multiple stages of the flow, and the equipment used in each stage.
Types of sulfide minerals
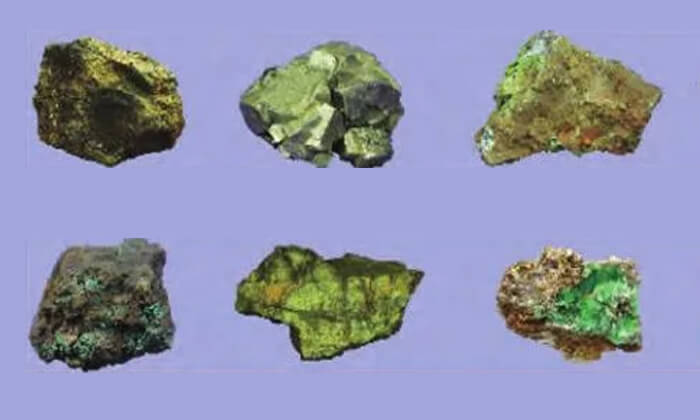

Sulfide minerals are divided into several types based on their chemical composition and structure. Some common types include pyrite, galena, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and bornite.
- Pyrite, also known as fool’s gold, is a popular sulfide mineral that typically forms brassy-yellow cubic crystals.
- Galena, another important sulfide mineral, is the primary ore of lead and has a metallic silvery-grey appearance.
- Chalcopyrite is a copper-iron sulfide mineral that is usually brassy-yellow in color.
- Sphalerite is a zinc sulfide mineral known for its many colors, ranging from dark brown to black or yellow-brown.
- Bornite is a copper-iron sulfide mineral that displays iridescent purple and blue colors when exposed to air.
These different sulfide minerals play vital roles in various beneficiation processes and are economically important in the global mining industry. However, sulfide ore beneficiation maximizes the economic value of mineral resources. In addition, sulfide ore beneficiation can extract valuable metals such as copper, lead, zinc and gold from low-grade ores that would otherwise be uneconomical to process. Through various processes such as crushing, grinding, and flotation, sulfide ore can be converted into high-quality concentrate and become a valuable commodity in the global market.
Sulfide mineral beneficiation methods
Sulfide ore beneficiation is a major challenge for the mining industry. Recovery of valuable minerals such as copper, lead-zinc or nickel from sulfide-bearing ores requires complex and costly processes with a wide range of potential risks. These challenges can include the presence of harmful gases such as hydrogen sulfide and carbon monoxide, as well as sulfuric acid and other wastes produced during processing. Other risks include material corrosion due to exposure to the chemicals used in the extraction process, which can deteriorate over time if not managed properly. Additionally, environmental contamination issues may arise if proper containment is not maintained throughout the process. Thus, the complexity of sulfide mineral processing has led to many modern innovations.
Beneficiation methods

Sulfide ore beneficiation is the process of separating and concentrating valuable minerals from other materials in an ore using physical or chemical processes.
- Flotation is very effective at recovering very fine gold particles that would otherwise be lost in traditional gravity separation methods.
- Another beneficiation process is cyanidation, which uses a solution of sodium cyanide to dissolve gold particles in the ore body, which are then separated using filters or centrifuges. Commonly used to separate and recover gold from sulfide deposits.
Another important beneficiation method is gravity separation, which uses density differences between minerals to separate them. This technique is particularly useful for large particles or when the density of the desired mineral is higher than the gangue material.
Other methods include magnetic separation and leaching processes, each with its own advantages and limitations depending on the specific mineral composition of the ore. Overall, the choice of beneficiation method depends on a variety of factors such as ore type, mineralogy and desired results.
The production index and equipment efficiency of flotation are high, and the recovery rate of sulfide minerals is very high. Flotation can be divided into forward flotation and reverse flotation: forward flotation is to float useful minerals into the foam product and leave gangue minerals in the slurry. On the contrary, it is reverse flotation. Commonly used flotation reagents in flotation mainly include regulators, collectors and frothers.
Sulfide Mineral Beneficiation Flow
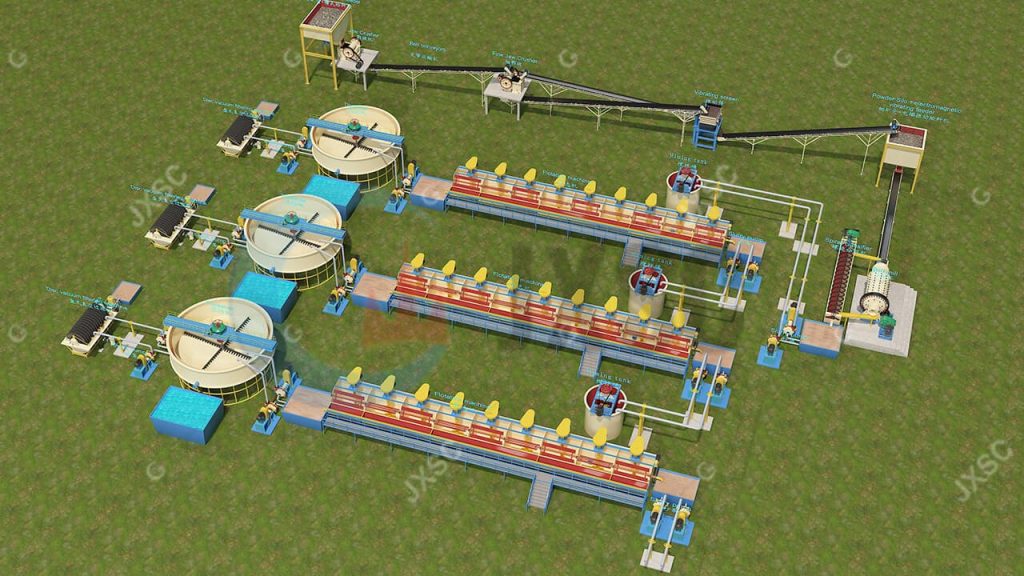
A complete processing plant consists of four systems:
1. Crushing system: 0-300mm material is stably and evenly fed from the feeder to the primary jaw crusher and crushed into a size of about 0-80mm. Then send it to the fine jaw crusher to crush the particles below 25mm again. The particles of +25mm are first conveyed to the vibrating screen for screening and then to the ball mill grinding system.
2. Grinding system: 0-25mm materials enter a storage bin before entering the ball mill. Enough 0-25mm materials are in the storage bin, and the crushing system can work separately from the grinding system. Then the 0-25mm material is sent into the ball mill through the swing feeder or the electromagnetic vibrating feeder through the belt conveyor. It needs to work together with the spiral classifier. The output from the overflow port of the classifier reaches 200 mesh, the bottom flow coarse particles are returned to the ball mill for grinding, and the circuit is closed. (The smaller the feed particle size of the ball mill, the better, and the grinding efficiency will be much higher.)
3. Flotation system: The 200-mesh material is first pumped from the slurry to the mixing tank to ensure that the material is thoroughly mixed. Add different agents in the flotation machine to separate other minerals. The flotation process has a three-stage flotation separation, which is to maximize the mineral grade.
4. Concentrate filtration system: After obtaining mineral concentrates from the flotation system for high-grade minerals. Concentrate using a thickener to make it denser. It is then sent to a disc vacuum filter to filter the water for more dry concentrated minerals. Then be dried in the sun or dried in a tumble dryer to obtain mineral concentrate.
The sulfide ore flotation plant is a concentrator that efficiently recovers sulfide ore. According to rock and mineral conditions, flow and capacity can be customized as small, medium and large according to requirements. It is generally used for processing sulfide rock gold, copper, silver, zinc, lead, fluorite and other ores; high recovery rate for sulfide minerals. According to the material situation, it can usually rut at 85-90%.
Sulfide ore flotation methods are extremely important in the mining industry. Efficient extraction of valuable metals from low-grade ores helps maximize resource utilization and reduce waste. Compared with traditional processing technologies, the combination of flotation, gravity separation, magnetic separation and other processes has higher recovery rates, thus improving the profitability of mining operations. The JXSC sulfide ore beneficiation process is usually more environmentally friendly than traditional methods. We will customize a beneficiation solutions and equipment based on your mineral situation. Contact us to get a quote!